SMPConv: Self-moving Point Representations for Continuous Convolution
Continuous convolution has recently gained prominence due to its ability to handle irregularly sampled data and model long-term dependency. Also, the promising experimental results of using large convolutional kernels have catalyzed the development of continuous convolution since they can construct large kernels very efficiently. Leveraging neural networks, more specifically multilayer perceptrons (MLPs), is by far the most prevalent approach to implementing continuous convolution. However, there are a few drawbacks, such as high computational costs, complex hyperparameter tuning, and limited descriptive power of filters. This paper suggests an alternative approach to building a continuous convolution without neural networks, resulting in more computationally efficient and improved performance. We present self-moving point representations where weight parameters freely move, and interpolation schemes are used to implement continuous functions. When applied to construct convolutional kernels, the experimental results have shown improved performance with drop-in replacement in the existing frameworks. Due to its lightweight structure, we are first to demonstrate the effectiveness of continuous convolution in a large-scale setting, e.g., ImageNet, presenting the improvements over the prior arts. Our code is available on https://github.com/sangnekim/SMPConv
PDF Abstract CVPR 2023 PDF CVPR 2023 Abstract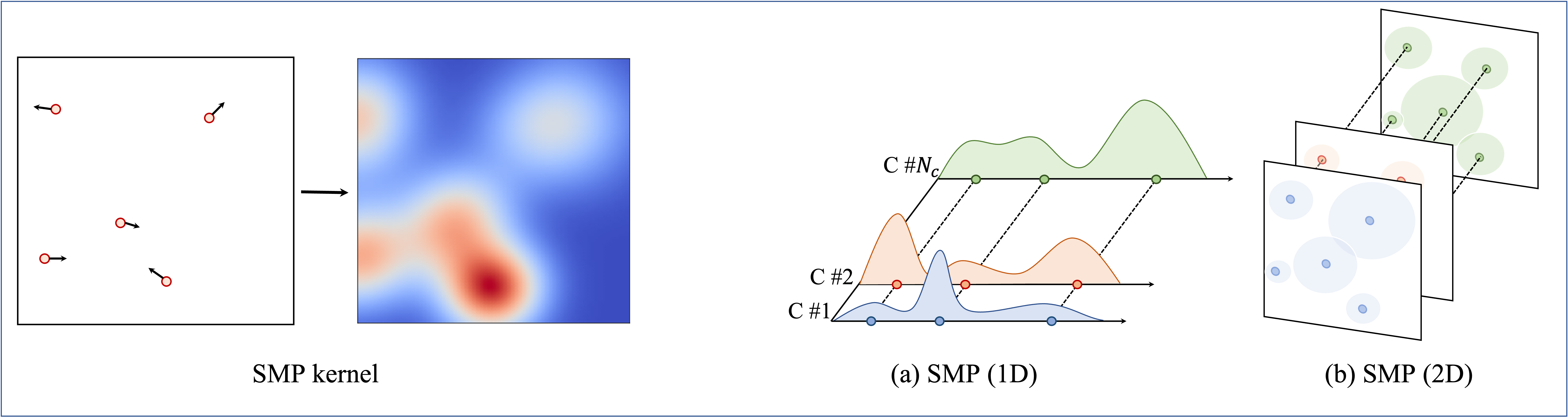







 CIFAR-10
CIFAR-10
 ImageNet
ImageNet
 MNIST
MNIST
