Online Graph Dictionary Learning
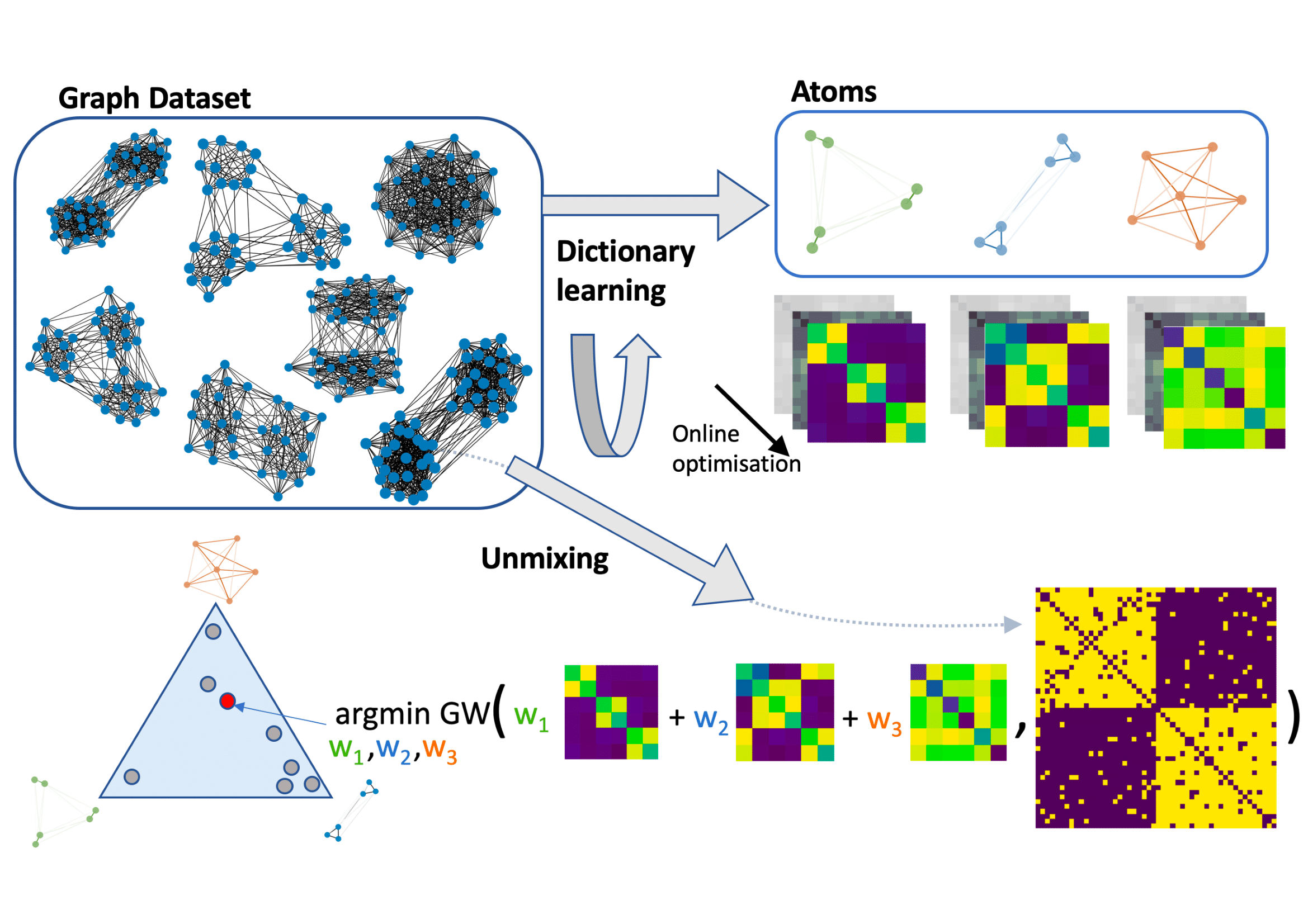
Dictionary learning is a key tool for representation learning, that explains the data as linear combination of few basic elements. Yet, this analysis is not amenable in the context of graph learning, as graphs usually belong to different metric spaces. We fill this gap by proposing a new online Graph Dictionary Learning approach, which uses the Gromov Wasserstein divergence for the data fitting term. In our work, graphs are encoded through their nodes' pairwise relations and modeled as convex combination of graph atoms, i.e. dictionary elements, estimated thanks to an online stochastic algorithm, which operates on a dataset of unregistered graphs with potentially different number of nodes. Our approach naturally extends to labeled graphs, and is completed by a novel upper bound that can be used as a fast approximation of Gromov Wasserstein in the embedding space. We provide numerical evidences showing the interest of our approach for unsupervised embedding of graph datasets and for online graph subspace estimation and tracking.
PDF Abstract