Balanced Spherical Grid for Egocentric View Synthesis
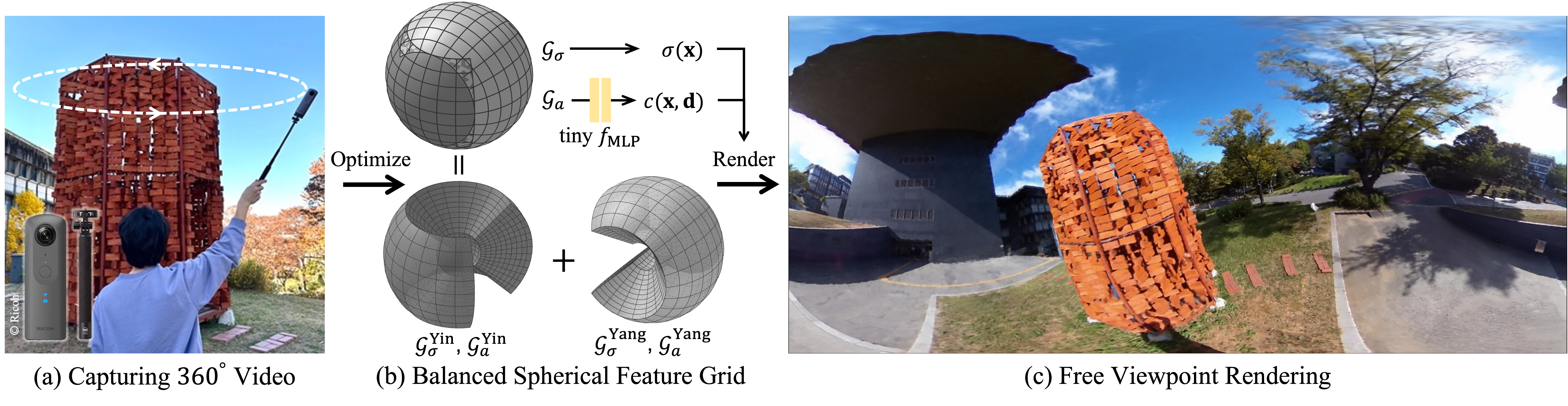
We present EgoNeRF, a practical solution to reconstruct large-scale real-world environments for VR assets. Given a few seconds of casually captured 360 video, EgoNeRF can efficiently build neural radiance fields which enable high-quality rendering from novel viewpoints. Motivated by the recent acceleration of NeRF using feature grids, we adopt spherical coordinate instead of conventional Cartesian coordinate. Cartesian feature grid is inefficient to represent large-scale unbounded scenes because it has a spatially uniform resolution, regardless of distance from viewers. The spherical parameterization better aligns with the rays of egocentric images, and yet enables factorization for performance enhancement. However, the na\"ive spherical grid suffers from irregularities at two poles, and also cannot represent unbounded scenes. To avoid singularities near poles, we combine two balanced grids, which results in a quasi-uniform angular grid. We also partition the radial grid exponentially and place an environment map at infinity to represent unbounded scenes. Furthermore, with our resampling technique for grid-based methods, we can increase the number of valid samples to train NeRF volume. We extensively evaluate our method in our newly introduced synthetic and real-world egocentric 360 video datasets, and it consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance.
PDF Abstract CVPR 2023 PDF CVPR 2023 Abstract